Run your first NodeTool workflow. No AI experience or coding needed.
You’ll:
- Run a complete workflow
- See results generate live
- Try different ways to work
- Understand the visual builder
For a visual overview first, see Start Here.
Step 1 — Install NodeTool
-
Download from nodetool.ai for macOS, Windows, or Linux
-
Run the installer - Sets up Python and AI engines automatically
-
Launch NodeTool - Default install location works for most people
Need help? See Installation Guide for GPU requirements and troubleshooting.
Install AI Models
For local workflows, install models:
- Open Models
- Install starter models:
- Flux or Qwen Image - Image generation (needs 8-12 GB VRAM)
- GPT-OSS - Text generation (optional)
- Wait for downloads (~20 GB)
No GPU? Skip local models. Use cloud services (OpenAI, Replicate) by adding API keys in Settings → Providers. See Hardware Requirements.
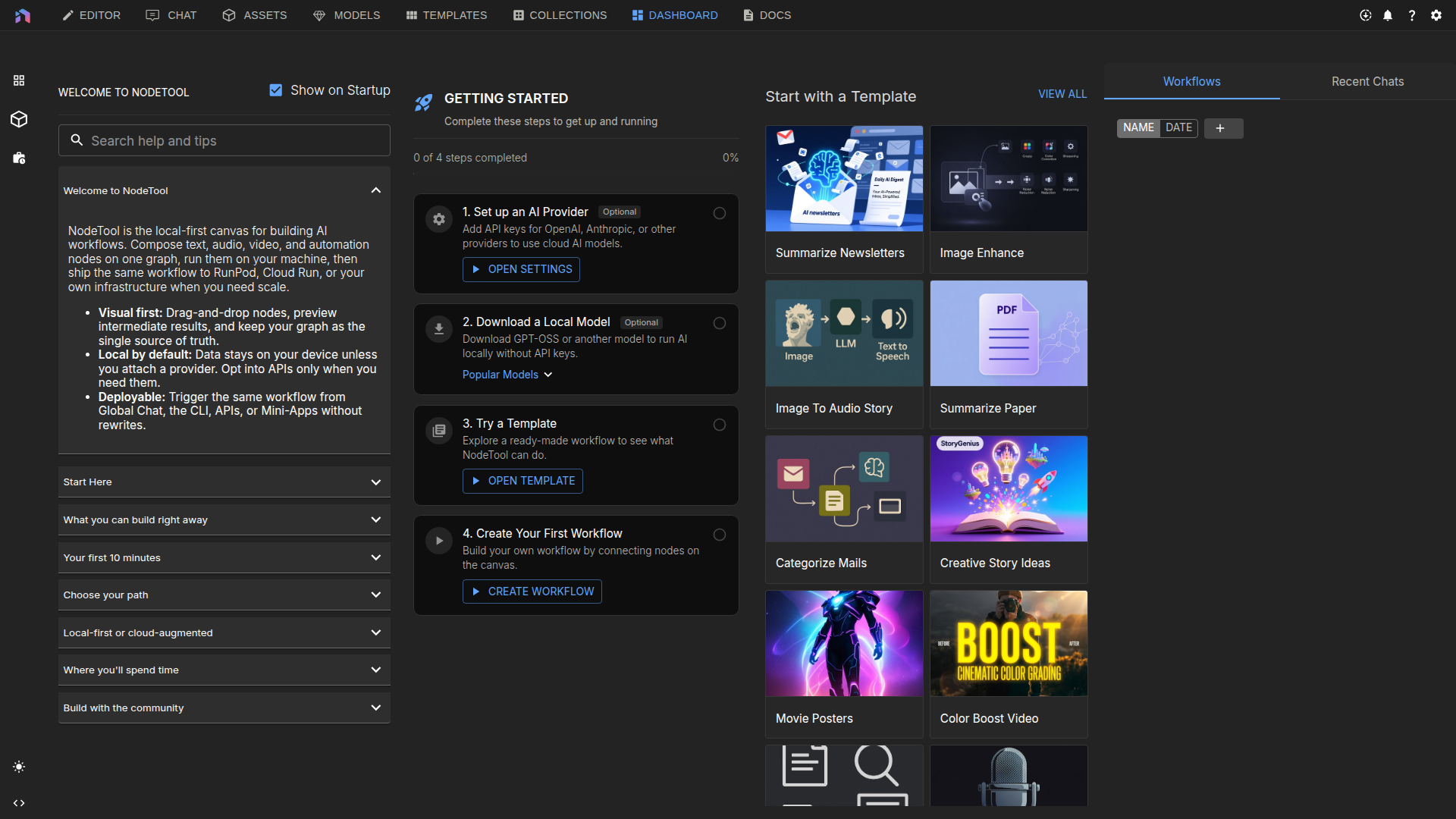
✅ You’re ready - Dashboard loaded with templates.
Step 2 — Run Your First Workflow
Pick one template to try:
Option A: Generate Movie Posters
- Find it: Dashboard → Templates → “Movie Posters”
- Open in Editor: See the workflow canvas
- How it works:
- Input nodes (left) - Describe your movie
- AI Strategy node (middle) - Plans the visual
- Image Generator (right) - Creates the poster
- Preview - Shows your result
- Try it: Click the input nodes and type:
- Title: “Ocean Depths”
- Genre: “Sci-Fi Thriller”
- Audience: “Adults who love mystery”
- Run: Click Run (bottom-right) or press Ctrl/⌘ + Enter
- Watch: Poster generates step by step
Option B: Creative Story Ideas
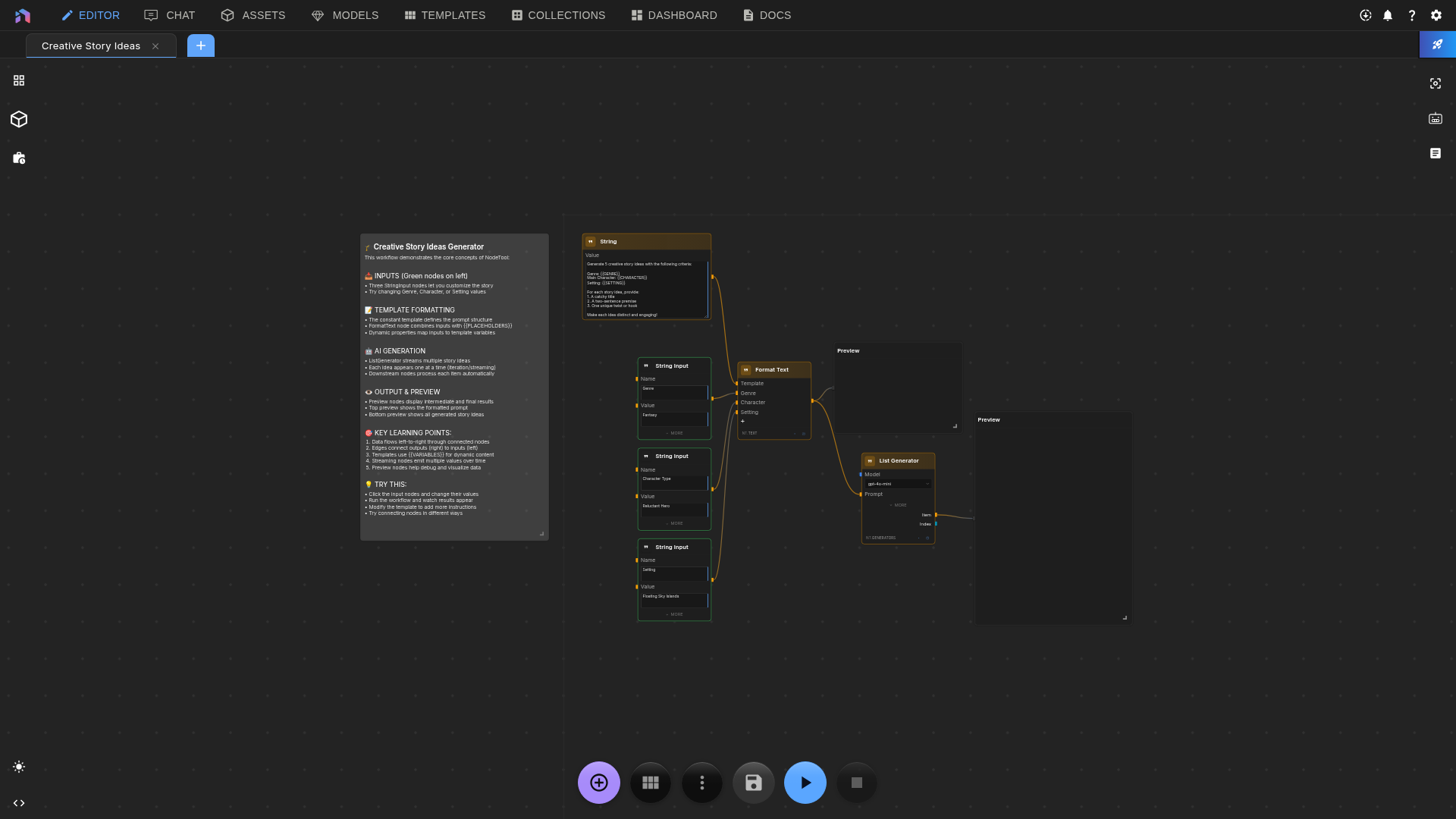
- Find it: Dashboard → Templates → “Creative Story Ideas”
- How it works:
- Input nodes - Your parameters
- AI Agent - Generates ideas
- Preview - Shows results
- Try it: Click the input nodes and type:
- Genre: “Cyberpunk”
- Character: “Rogue AI detective”
- Setting: “Neon-lit underwater city”
- Run: Click Run or Ctrl/⌘ + Enter
- Watch: Ideas appear one at a time
✅ Done - You ran your first workflow.
Step 3 — Customize and Iterate
-
Save: Press Ctrl/⌘ + S and name it
-
Change things: Edit inputs and run again
-
Explore:
- Click nodes to see settings
- Hover connections to see data flow
- Click Preview nodes for intermediate results
Workflows are reusable. Try variations. Refine. Save.
✅ Done - You can customize workflows.
Step 4 — Share as a Mini-App
Convert a workflow into a simplified interface:
- Open your workflow in the editor
- Click Mini-App (top-right)
- See simplified view: Only inputs and outputs, no graph
Mini-Apps hide complexity. Others can use your workflow without seeing how it works.
✅ Done - You know three ways to work: Visual Editor (full control), Mini-App (simple interface).
What You Learned
- Installed NodeTool and models
- Ran a workflow
- Understood nodes and connections
- Customized inputs
- Shared as a Mini-App
Next Steps
Learn more:
- Key Concepts - How workflows really work
- User Interface - Every tool explained
- Workflow Editor - Build from scratch
- Tips & Tricks - Power user moves
Try examples:
- Workflow Gallery - 19+ ready workflows
- Workflow Patterns - Common patterns
- Node Library - All available nodes
Go deeper:
- Models & Providers - Set up more models
- Asset Management - Organize files
- Deployment - Share with the world
Get help:
- Workflow Debugging - Fix problems
- Troubleshooting - Common issues
- Glossary - Plain-English terms
- Discord - Ask the community
- GitHub Issues - Report bugs
